实验环境
- torch = 1.6.0
- torchvision = 0.7.0
- matplotlib = 3.3.3 # 绘图用
- progressbar = 2.5 # 绘制进度条用
- easydict # 超参数字典功能增强
使用数据集
导入相关的包
# 导包
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torchvision
from torchvision import datasets,transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
from progressbar import *
设置超参数
from easydict import EasyDict #增强python的dict的功能用
# 定义超参数
super_param = {
"batch_size":256,
"device": torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'),
"epochs":10,
"lr":0.3,
}
super_param = EasyDict(super_param)
print(super_param)
{'batch_size': 16, 'device': device(type='cuda', index=0), 'epochs': 10, 'lr': 0.3, 'hidden_num': 15}
数据处理(下载、处理、加载数据到DataLoader)
# 下载、加载数据
# 构transform(pipeline),对图像做处理
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,),(0.3081,)) #正则化
])
# 下载数据
trainsets = datasets.MNIST('data',train=True,download=True,transform=transform)
testsets = datasets.MNIST('data',train=False,download=True,transform=transform)
# dataloader 加载数据
train_loader = DataLoader(trainsets,batch_size=super_param.batch_size,shuffle=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(trainsets,batch_size=super_param.batch_size,shuffle=True)
查看数据样例
查看数据样例【单张】
# 查看数据样例-单张
image,label = trainsets[random.randint(0,len(trainsets))]
print('label=',label)
plt.imshow(image.permute(1,2,0),cmap='gray')
plt.show()
查看数据样例【一批】
# 查看数据样例-一批
images,labels = next(iter(test_loader))
data_sample_img = torchvision.utils.make_grid(images).numpy().transpose(1,2,0)
print('labels=',labels)
plt.figure(dpi=200)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.imshow(data_sample_img)
plt.show()

构建CNN网络模型 -简单版- 使用Sequential
## 构建CNN模型-简单版-使用Sequential
model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1,out_channels=10,kernel_size=5,stride=1,padding=0),# b*1*28*28-->b*10*24*24
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),# b*10*24*24-->b*10*12*12
nn.Conv2d(10,20,3,1,0),# b*10*12*12-->b*20*10*10
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Flatten(),#b*20*10*10-->b*2000
nn.Linear(2000,500),#b*2000-->b*500
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(500,10),#b*500-->b*10
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Softmax(),
)
print(model)
Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU()
(2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(3): Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
(4): ReLU()
(5): Flatten(start_dim=1, end_dim=-1)
(6): Linear(in_features=2000, out_features=500, bias=True)
(7): ReLU()
(8): Linear(in_features=500, out_features=10, bias=True)
(9): ReLU()
(10): Softmax(dim=None)
)
构建CNN网络模型 -使用自定义类
# 构建网络模型 - 使用自定义类
class Digit_Rec(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Digit_Rec,self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1,10,5) #1:灰度图片的通道,10:输出通道,5:kernel
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU()
self.max_pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2,2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(10,20,3) #10:输入通道,20:输出通道,3:Kernel
self.relu2 = nn.ReLU()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(20*10*10,500) # 20*10*10:输入通道,500:输出通道
self.relu3 = nn.ReLU()
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(500,10) # 500:输入通道,10:输出通道
self.relu4 = nn.ReLU()
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self,x):
batch_size = x.size(0) # x的格式:batch_size x 1 x 28 x 28 拿到了batch_size
x = self.conv1(x) # 输入:batch*1*28*28 输出:batch*10*24*24
x = self.relu1(x)
x = self.max_pool(x) # 输入:batch*10*24*24输出:batch*10*12*12
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.relu2(x)
x = x.view(batch_size,-1) #fatten 展平 -1自动计算维度,20*10*10=2000
x = self.fc1(x) # 输入:batch*2000 输出:batch*500
x = self.relu3(x)
x = self.fc2(x) # 输入:batch*500 输出:batch*10
x = self.relu4(x)
output = self.softmax(x) # 计算分类后,每个数字的概率值
return output
model = Digit_Rec()
print(model)
Digit_Rec(
(conv1): Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(relu1): ReLU()
(max_pool): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(conv2): Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
(relu2): ReLU()
(fc1): Linear(in_features=2000, out_features=500, bias=True)
(relu3): ReLU()
(fc2): Linear(in_features=500, out_features=10, bias=True)
(relu4): ReLU()
(softmax): Softmax(dim=1)
)
定义损失函数和优化器
# 定义损失函数和优化
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=super_param.lr)
定义模型训练单个epoch函数
# 定义模型训练单个epoch函数
def train_model_epoch(model,train_loader,super_param,criterion,optimzer,epoch):
model.train()#训练声明
for batch_index,(images,labels) in enumerate(train_loader):
# 数据上device
images,labels = images.to(super_param.device),labels.to(super_param.device)
# 梯度清零
optimzer.zero_grad()
# 前向传播
output = model(images)
# 计算损失
loss = criterion(output,labels)
# 反向传播,计算梯度
loss.backward()
# 参数更新(优化)
optimzer.step()
# 打印训练参考信息,每1000个batch打印一次
if batch_index % 1000 == 0:
print("Epoch:{} Batch Index(batch_size={}):{}/{} Loss:{}".
format(epoch,super_param.batch_size,batch_index,len(train_loader),loss.item()))
定义模型验证方法
# 定义模型验证方法
def test_model(model,test_loader,super_param,criterion):
model.eval()#测试声明
# 数据统计
correct_num,test_loss = 0.0,0.0 #正确数,测试损失
#定义进度条
widgets = ['模型测试中: ',Percentage(), ' ', Bar('#'),' ', Timer(),' ', ETA()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=100).start()
# 取消计算梯度,避免更新模型参数
with torch.no_grad():
for batch_index,(images,labels) in enumerate(test_loader):
# 数据上devics
images,labels = images.to(super_param.device),labels.to(super_param.device)
# 模型预测
output = model(images)
# 计算测试损失
test_loss += criterion(output,labels).item()
# 确定预测结果是哪个数字
pred = output.argmax(dim=1) #argmax返回 值,索引 dim=1表示要索引
# 统计预测正确数量
correct_num += pred.eq(labels.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
#更新进度条进度
pbar.update(batch_index/len(test_loader)*100)
#释放进度条
pbar.finish()
#打印测试信息
test_loss = test_loss/len(test_loader.dataset)
test_accuracy = correct_num / len(test_loader.dataset)
print("Test --- Avg Loss:{},Accuracy:{}\n".format(test_loss,test_accuracy))
return test_loss,test_accuracy
模型训练和测试
# 模型训练和测试
#模型上device
mode = model.to(super_param.device)
#记录每个epoch的测试数据、用于绘图
epoch_list = []
loss_list = []
accuracy_list = []
for epoch in range(super_param.epochs):
train_model_epoch(model,train_loader,super_param,criterion,optimizer,epoch)
test_loss,test_accuracy = test_model(model,test_loader,super_param,criterion)
# 数据统计
epoch_list.append(epoch)
loss_list.append(test_loss)
accuracy_list.append(test_accuracy)
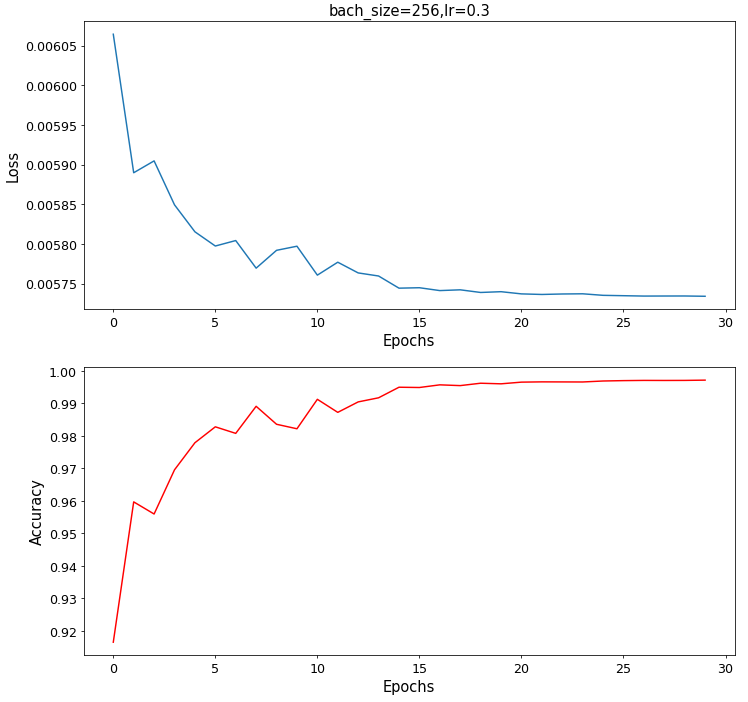
查看数据统计结果
# 查看数据统计结果
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,12),dpi=70)
#子图1
ax1 = plt.subplot(2,1,1)
title = "bach_size={},lr={}".format(super_param.batch_size,super_param.lr)
plt.title(title,fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel('Epochs',fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel('Loss',fontsize=15)
plt.xticks(fontsize=13)
plt.yticks(fontsize=13)
plt.plot(epoch_list,loss_list)
#子图2
ax2 = plt.subplot(2,1,2)
plt.xlabel('Epochs',fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel('Accuracy',fontsize=15)
plt.xticks(fontsize=13)
plt.yticks(fontsize=13)
plt.plot(epoch_list,accuracy_list,'r')
plt.show()




测试
非常不错