1.K-means算法
- 具体介绍参考:Kmeans算法简介
k-means聚类的算法运行过程:
(1)选择k个初始聚类中心 (2)计算每个对象与这k个中心各自的距离,按照最小距离原则分配到最邻近聚类 (3)使用每个聚类中的样本均值作为新的聚类中心 (4)重复步骤(2)和(3)直到聚类中心不再变化 (5)结束,得到k个聚类
2.算法实现
2.1数据加载
- 函数封装
# STEP1:加载数据集,获取所有box的width、height
import os
from progressbar import *
import xmltodict
import numpy as np
def load_dataset(data_root):
xml_dir= os.path.join(data_root,"Annotations") #xml文件路径(Annotations)
width_height_list = [] #用于存储统计结果
#进度条功能
widgets = ['box width_height 统计: ',Percentage(), ' ', Bar('#'),' ', Timer(),' ', ETA()]
pbar = ProgressBar(widgets=widgets, maxval=len(os.listdir(xml_dir))).start()
count = 0
for xml_file in os.listdir(xml_dir):
# 拼接xml文件的path
xml_file_path = os.path.join(xml_dir,xml_file)
# 读取xml文件到字符串
with open(xml_file_path) as f:
xml_str = f.read()
# xml字符串转为字典
xml_dic = xmltodict.parse(xml_str)
# 获取图片的width、height
img_width = float(xml_dic["annotation"]["size"]["width"])
img_height = float(xml_dic["annotation"]["size"]["height"])
# 获取xml文件中的所有objects
obj_list = []
objects = xml_dic["annotation"]["object"]
if isinstance(objects,list): # xml文件中包含多个object
for obj in objects:
obj_list.append(obj)
else: # xml文件中包含1个object
obj_list.append(objects)
#print(obj_list)
# width_height布统计
for obj in obj_list:
#box 的height\width归一化
box_width = (float(obj['bndbox']["xmax"]) - float(obj['bndbox']["xmin"]))/img_width
box_height = (float(obj['bndbox']["ymax"]) - float(obj['bndbox']["ymin"]))/img_height
width_height_list.append([box_width,box_height])
#更新进度条
count += 1
pbar.update(count)
#释放进度条
pbar.finish()- 调用效果
#输出统计结果信息
data_root = "/data/jupiter/project/dataset/209_VOC_new"
width_height_list = load_dataset(data_root)
width_height_np = np.array(width_height_list)
print("clustering feature data is ready. shape = (N object, width and height) = {}".format(width_height_np.shape))box width_height 统计: 100% |###############| Elapsed Time: 0:00:35 Time: 0:00:35
clustering feature data is ready. shape = (N object, width and height) = (10670, 2)2.2 将未聚类前的统计结果绘图表示
# 将未聚类前的统计结果绘图表示
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
plt.scatter(width_height_np[:,0],width_height_np[:,1],alpha=0.3)
plt.title("Clusters",fontsize=20)
plt.xlabel("normalized width",fontsize=20)
plt.ylabel("normalized height",fontsize=20)
plt.show()- 调用效果

2.3 实现距离评估函数(这里用的是iou)
这里iou的计算公式为:
$$ \begin{array}{rl} IoU &= \frac{\textrm{intersection} }{ \textrm{union} - \textrm{intersection} }\\ \textrm{intersection} &= Min(w_1,w_2) Min(h_1,h_2)\\ \textrm{union} & = w_1 h_1 + w_2 h_2 \end{array} $$
- 图示
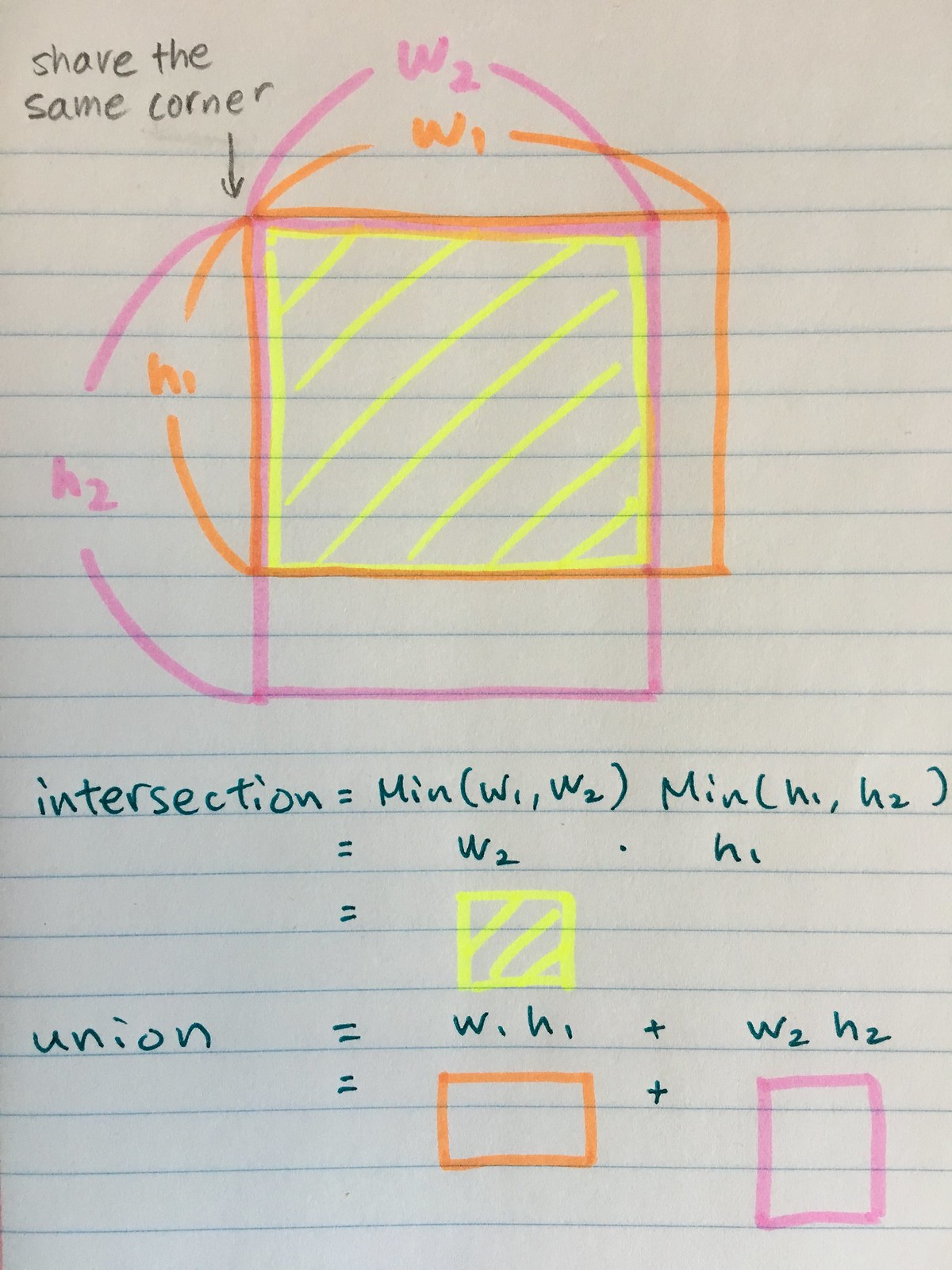
- 代码实现
import numpy as np
# 数据间距离评估函数
def iou(box, clusters):
"""
计算一个ground truth边界盒和k个先验框(Anchor)的交并比(IOU)值。
参数box: 元组或者数据,代表ground truth的长宽。
参数clusters: 形如(k,2)的numpy数组,其中k是聚类Anchor框的个数
返回:ground truth和每个Anchor框的交并比。
"""
x = np.minimum(clusters[:, 0], box[0])
y = np.minimum(clusters[:, 1], box[1])
if np.count_nonzero(x == 0) > 0 or np.count_nonzero(y == 0) > 0:
raise ValueError("Box has no area")
intersection = x * y
box_area = box[0] * box[1]
cluster_area = clusters[:, 0] * clusters[:, 1]
iou_ = intersection / (box_area + cluster_area - intersection)
return iou_2.4实现kmeans聚类函数
# 实现kmeans聚类函数
def kmeans(boxes, k):
"""
利用IOU值进行K-means聚类
参数boxes: 形状为(r, 2)的ground truth框,其中r是ground truth的个数
参数k: Anchor的个数
返回值:形状为(k, 2)的k个Anchor框
"""
# 即是上面提到的r
rows = boxes.shape[0]
# 距离数组,计算每个ground truth和k个Anchor的距离
distances = np.empty((rows, k))
# 上一次每个ground truth"距离"最近的Anchor索引
last_clusters = np.zeros((rows,))
# 设置随机数种子
np.random.seed()
# 初始化聚类中心,k个簇,从r个ground truth随机选k个
clusters = boxes[np.random.choice(rows, k, replace=False)]
# 开始聚类
while True:
# 计算每个ground truth和k个Anchor的距离,用1-IOU(box,anchor)来计算
for row in range(rows):
distances[row] = 1 - iou(boxes[row], clusters)
# 对每个ground truth,选取距离最小的那个Anchor,并存下索引
nearest_clusters = np.argmin(distances, axis=1)
# 如果当前每个ground truth"距离"最近的Anchor索引和上一次一样,聚类结束
if (last_clusters == nearest_clusters).all():
break
# 更新簇中心为簇里面所有的ground truth框的均值
for cluster in range(k):
clusters[cluster] = np.median(boxes[nearest_clusters == cluster], axis=0)
# 更新每个ground truth"距离"最近的Anchor索引
last_clusters = nearest_clusters
return clusters,nearest_clusters2.4 调用测试
CLUSTERS = 9 #聚类数量,anchor数量
INPUTDIM = 416 #输入网络大小
clusters_center_list,nearest_clusters = kmeans(width_height_np, k=CLUSTERS)
clusters_center_list_handle = np.array(clusters_center_list)*INPUTDIM
# 得到最终填入YOLOv3 的cfg文件中的anchor
print('Boxes:')
print(clusters_center_list_handle.astype(np.int32)) Boxes:
[[ 9 37]
[235 239]
[ 4 30]
[ 24 33]
[ 5 21]
[ 52 63]
[ 5 26]
[ 7 28]
[ 6 33]]2.5聚类结果绘制与效果评估(mean_iou)
- 查看数据聚类结果
import seaborn as sns
current_palette = list(sns.xkcd_rgb.values())
def plot_cluster_result(plt,clusters,nearest_clusters,mean_iou,width_height_np,k):
for icluster in np.unique(nearest_clusters):
pick = nearest_clusters==icluster
c = current_palette[icluster]
plt.rc('font', size=8)
plt.plot(width_height_np[pick,0],width_height_np[pick,1],"p",
color=c,
alpha=0.5,label="cluster = {}, N = {:6.0f}".format(icluster,np.sum(pick)))
plt.text(clusters[icluster,0],
clusters[icluster,1],
"c{}".format(icluster),
fontsize=20,color="red")
plt.title("Clusters=%d" %k)
plt.xlabel("width")
plt.ylabel("height")
plt.legend(title="Mean IoU = {:5.4f}".format(mean_iou))
# achor结果评估
def avg_iou(boxes, clusters):
"""
计算一个ground truth和k个Anchor的交并比的均值。
"""
return np.mean([np.max(iou(boxes[i], clusters)) for i in range(boxes.shape[0])])
figsize = (7,5)
plt.figure(figsize=figsize)
mean_iou = avg_iou(width_height_np, out)
plot_cluster_result(plt,clusters_center_list,nearest_clusters,mean_iou,width_height_np,k=CLUSTERS)- 运行效果

- 查看聚类中心分布
w = width_height_np[:, 0].tolist()
h = width_height_np[:, 1].tolist()
centroid_w=clusters_center_list[:,0].tolist()
centroid_h=clusters_center_list[:,1].tolist()
plt.figure(dpi=200)
plt.title("kmeans")
plt.scatter(w, h, s=10, color='b')
plt.scatter(centroid_w,centroid_h,s=10,color='r')
plt.show()- 运行效果

3.汇总简略版
#coding=utf-8
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import numpy as np
import glob
def iou(box, clusters):
"""
计算一个ground truth边界盒和k个先验框(Anchor)的交并比(IOU)值。
参数box: 元组或者数据,代表ground truth的长宽。
参数clusters: 形如(k,2)的numpy数组,其中k是聚类Anchor框的个数
返回:ground truth和每个Anchor框的交并比。
"""
x = np.minimum(clusters[:, 0], box[0])
y = np.minimum(clusters[:, 1], box[1])
if np.count_nonzero(x == 0) > 0 or np.count_nonzero(y == 0) > 0:
raise ValueError("Box has no area")
intersection = x * y
box_area = box[0] * box[1]
cluster_area = clusters[:, 0] * clusters[:, 1]
iou_ = intersection / (box_area + cluster_area - intersection)
return iou_
def avg_iou(boxes, clusters):
"""
计算一个ground truth和k个Anchor的交并比的均值。
"""
return np.mean([np.max(iou(boxes[i], clusters)) for i in range(boxes.shape[0])])
def kmeans(boxes, k):
"""
利用IOU值进行K-means聚类
参数boxes: 形状为(r, 2)的ground truth框,其中r是ground truth的个数
参数k: Anchor的个数
参数dist: 距离函数
返回值:形状为(k, 2)的k个Anchor框
"""
# 即是上面提到的r
rows = boxes.shape[0]
# 距离数组,计算每个ground truth和k个Anchor的距离
distances = np.empty((rows, k))
# 上一次每个ground truth"距离"最近的Anchor索引
last_clusters = np.zeros((rows,))
# 设置随机数种子
np.random.seed()
# 初始化聚类中心,k个簇,从r个ground truth随机选k个
clusters = boxes[np.random.choice(rows, k, replace=False)]
# 开始聚类
while True:
# 计算每个ground truth和k个Anchor的距离,用1-IOU(box,anchor)来计算
for row in range(rows):
distances[row] = 1 - iou(boxes[row], clusters)
# 对每个ground truth,选取距离最小的那个Anchor,并存下索引
nearest_clusters = np.argmin(distances, axis=1)
# 如果当前每个ground truth"距离"最近的Anchor索引和上一次一样,聚类结束
if (last_clusters == nearest_clusters).all():
break
# 更新簇中心为簇里面所有的ground truth框的均值
for cluster in range(k):
clusters[cluster] = np.median(boxes[nearest_clusters == cluster], axis=0)
# 更新每个ground truth"距离"最近的Anchor索引
last_clusters = nearest_clusters
return clusters
# 加载自己的数据集,只需要所有labelimg标注出来的xml文件即可
def load_dataset(path):
dataset = []
for xml_file in glob.glob("{}/*xml".format(path)):
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
# 图片高度
height = int(tree.findtext("./size/height"))
# 图片宽度
width = int(tree.findtext("./size/width"))
for obj in tree.iter("object"):
# 偏移量
xmin = int(obj.findtext("bndbox/xmin")) / width
ymin = int(obj.findtext("bndbox/ymin")) / height
xmax = int(obj.findtext("bndbox/xmax")) / width
ymax = int(obj.findtext("bndbox/ymax")) / height
xmin = np.float64(xmin)
ymin = np.float64(ymin)
xmax = np.float64(xmax)
ymax = np.float64(ymax)
if xmax == xmin or ymax == ymin:
print(xml_file)
# 将Anchor的长宽放入dateset,运行kmeans获得Anchor
dataset.append([xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin])
return np.array(dataset)
ANNOTATIONS_PATH = "/data/jupiter/project/dataset/209_VOC_new/Annotations" #xml文件所在文件夹
CLUSTERS = 9 #聚类数量,anchor数量
INPUTDIM = 416 #输入网络大小
data = load_dataset(ANNOTATIONS_PATH)
out = kmeans(data, k=CLUSTERS)
print('Boxes:')
out_handle = np.array(out)*INPUTDIM
print(out_handle.astype(np.int32))
print("Accuracy: {:.2f}%".format(avg_iou(data, out) * 100))
final_anchors = np.around(out[:, 0] / out[:, 1], decimals=2).tolist()
print("Before Sort Ratios:\n {}".format(final_anchors))
print("After Sort Ratios:\n {}".format(sorted(final_anchors)))Boxes:
[[ 8 34]
[234 256]
[279 239]
[ 52 63]
[ 6 28]
[ 5 26]
[ 24 33]
[ 10 37]
[177 216]]
Accuracy: 82.93%
Before Sort Ratios:
[0.24, 0.92, 1.17, 0.83, 0.23, 0.19, 0.74, 0.28, 0.82]
After Sort Ratios:
[0.19, 0.23, 0.24, 0.28, 0.74, 0.82, 0.83, 0.92, 1.17]
评论 (0)