1.nginx默认配置文件
Nginx默认的配置文件是在安装目录下的 conf目录下,后续对 Nginx的使用基本上都是对此配置文件进行相应的修改,修改过nginx.conf配置文件,记得要重启Nginx服务(☆☆☆☆☆)
默认的配置文件内容(其中#开头的都是被注释了的内容):
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}2.nginx配置文件配置详解
nginx配置文件主要分为如下三部分
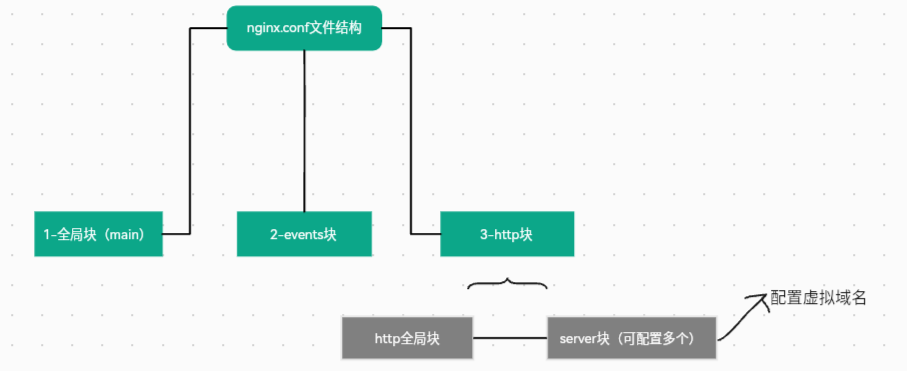
2.1 全局块
全局块是默认配置文件从开始到events块之间的内容。主要设置nginx整体运行的配置指令,这些指令的作用域是全局,配置案例解析
#定义Nginx运行的用户和用户组
user www www;
#nginx进程数,建议设置为等于CPU总核心数。
worker_processes 8;
#全局错误日志定义类型,[ debug | info | notice | warn | error | crit ]
error_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log info;
#进程pid文件
pid /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid;
#指定进程可以打开的最大描述符:数目
#工作模式与连接数上限
#这个指令是指当一个nginx进程打开的最多文件描述符数目,理论值应该是最多打开文件数(ulimit -n)与nginx进程数相除,但是nginx分配请求并不是那么均匀,所以最好与ulimit -n 的值保持一致。
#现在在linux 2.6内核下开启文件打开数为65535,worker_rlimit_nofile就相应应该填写65535。
#这是因为nginx调度时分配请求到进程并不是那么的均衡,所以假如填写10240,总并发量达到3-4万时就有进程可能超过10240了,这时会返回502错误。
worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;2.2 events块
events块的指令主要影响nginx服务器和用户的网络连接,对性能影响较大。配置案例:
events
{
#参考事件模型,use [ kqueue | rtsig | epoll | /dev/poll | select | poll ]; epoll模型
#是Linux 2.6以上版本内核中的高性能网络I/O模型,linux建议epoll,如果跑在FreeBSD上面,就用kqueue模型。
#补充说明:
#与apache相类,nginx针对不同的操作系统,有不同的事件模型
#A)标准事件模型
#Select、poll属于标准事件模型,如果当前系统不存在更有效的方法,nginx会选择select或poll
#B)高效事件模型
#Kqueue:使用于FreeBSD 4.1+, OpenBSD 2.9+, NetBSD 2.0 和 MacOS X.使用双处理器的MacOS X系统使用kqueue可能会造成内核崩溃。
#Epoll:使用于Linux内核2.6版本及以后的系统。
#/dev/poll:使用于Solaris 7 11/99+,HP/UX 11.22+ (eventport),IRIX 6.5.15+ 和 Tru64 UNIX 5.1A+。
#Eventport:使用于Solaris 10。 为了防止出现内核崩溃的问题, 有必要安装安全补丁。
use epoll;
#单个进程最大连接数(最大连接数=连接数*进程数)
#根据硬件调整,和前面工作进程配合起来用,尽量大,但是别把cpu跑到100%就行。每个进程允许的最多连接数,理论上每台nginx服务器的最大连接数为。
worker_connections 65535;
#keepalive超时时间。
keepalive_timeout 60;
#客户端请求头部的缓冲区大小。这个可以根据你的系统分页大小来设置,一般一个请求头的大小不会超过1k,不过由于一般系统分页都要大于1k,所以这里设置为分页大小。
#分页大小可以用命令getconf PAGESIZE 取得。
#[root@web001 ~]# getconf PAGESIZE
#4096
#但也有client_header_buffer_size超过4k的情况,但是client_header_buffer_size该值必须设置为“系统分页大小”的整倍数。
client_header_buffer_size 4k;
#这个将为打开文件指定缓存,默认是没有启用的,max指定缓存数量,建议和打开文件数一致,inactive是指经过多长时间文件没被请求后删除缓存。
open_file_cache max=65535 inactive=60s;
#这个是指多长时间检查一次缓存的有效信息。
#语法:open_file_cache_valid time 默认值:open_file_cache_valid 60 使用字段:http, server, location 这个指令指定了何时需要检查open_file_cache中缓存项目的有效信息.
open_file_cache_valid 80s;
#open_file_cache指令中的inactive参数时间内文件的最少使用次数,如果超过这个数字,文件描述符一直是在缓存中打开的,如上例,如果有一个文件在inactive时间内一次没被使用,它将被移除。
#语法:open_file_cache_min_uses number 默认值:open_file_cache_min_uses 1 使用字段:http, server, location 这个指令指定了在open_file_cache指令无效的参数中一定的时间范围内可以使用的最小文件数,如果使用更大的值,文件描述符在cache中总是打开状态.
open_file_cache_min_uses 1;
#语法:open_file_cache_errors on | off 默认值:open_file_cache_errors off 使用字段:http, server, location 这个指令指定是否在搜索一个文件时记录cache错误.
open_file_cache_errors on;
}常用到的配置案例:
events { # events块开始
worker_connections 1024; #每个工作进程的最大连接数量(根据硬件调整,和前面工作进程配合起来用,尽量大,但是别把cpu跑到100%就行。)
use epoll; # 使用epoll的I/O 模型。linux建议epoll,FreeBSD建议采用kqueue,window下不指定。
accept_mutex on; #开启网络连接的序列化(防止多个进程对连接的争抢)
multi_accept on; #允许同时接收多个网络连接(默认关闭),工作进程都有能力同时接收多个新到达的网络连接
} 2.3 http块
这部分是 Nginx 服务器配置中最频繁的部分,代理、缓存和日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置都在这里。需要注意的是:http 块也可以包括 http 全局块、server 块。下面的反向代理、动静分离、负载均衡都是在这部分中配置
http全局块:http全局块配置的指令包括:文件引入、MIME-TYPE定义、日志自定义、连接超时时间、单链接请求数上限等。server块:这块和虚拟主机有密切关系,从用户角度看,虚拟主机和一台独立的硬件主机是完全一样的,该技术的产生是为了节省互联网服务器硬件成本。- 每个
http块可以包括多个server块,而每个server块就相当于一个虚拟主机。 - 每个
server块也分为全局server块,以及可以同时包含多个locaton块。
2.3.1 http块全局配置
配置案例:
#文件扩展名与文件类型映射表
include mime.types;
#默认文件类型
default_type application/octet-stream;
#默认编码
#charset utf-8;
#设定通过nginx上传文件的大小
client_max_body_size 8m;
#开启高效文件传输模式,sendfile指令指定nginx是否调用sendfile函数来输出文件,对于普通应用设为 on,如果用来进行下载等应用磁盘IO重负载应用,可设置为off,以平衡磁盘与网络I/O处理速度,降低系统的负载。注意:如果图片显示不正常把这个改成off。
#sendfile指令指定 nginx 是否调用sendfile 函数(zero copy 方式)来输出文件,对于普通应用,必须设为on。如果用来进行下载等应用磁盘IO重负载应用,可设置为off,以平衡磁盘与网络IO处理速度,降低系统uptime。
sendfile on;
#开启目录列表访问,合适下载服务器,默认关闭。
autoindex on;
# 负载均衡服务器组配置
upstream backend {
server 127.0.0.1:8081 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=10s;
server 127.0.0.1:8082 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=10s;
# 可选的其他参数
# least_conn; # 使用最少连接的服务器
# ip_hash; # 根据客户端IP进行哈希,确保来自同一IP的请求总是发送到同一台服务器
# keepalive 32; # 每个worker进程保持的最大空闲连接数
}2.3.2 http块下的server块
server块 必须包含在http之下。server是一切的开始,代表一个代理的出现,里边两大配置项:listen监听接口和server_name监听的地址,里边还包括了location和其它配置项,当存在server的时候,nginx获取到的请求都会去匹配这些server(匹配其中的listen和server_name)。
- server也可单独拆分为一个文件 在nginx下http块下引用即可
location是nginx的精华,nginx就是通过拦截到的请求去对配置好的location块进行请求代理的。
- alias&root:将请求代理到本地的指令,也就是如果可以把请求发送到你的 硬盘里去获取资源,这个指令可以代理前端的静态资源
- proxy_pass:对请求进行转发重定向的
- rewrite:用来重写请求路径
配置案例:
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html/dist;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# 反向代理+负载均衡配置
location /api/ {
rewrite ^/api/(.*)$ /$1 break;
proxy_pass http://backend;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header REMOTE-HOST $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
}
location /upload/ {
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
# 请求日志按天/按小时/按分钟/按秒分割
if ($time_iso8601 ~ "^(\d{4})-(\d{2})-(\d{2})T(\d{2}):(\d{2}):(\d{2})")
{
set $year $1;
set $month $2;
set $day $3;
set $hour $4;
set $minutes $5;
set $seconds $6;
}
access_log ./logs/nginx-access_$year-$month-$day.log;
# 错误日志配置
error_log ./logs/nginx-access-error.log;
}3.nginx 反向代理配置
通过server>location>proxy_pass属性生效:
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header REMOTE-HOST $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
}
}还可以针对单个子路径进行反向代理配置
server {
listen 9001;
server_name localhost;
location ~ /edu/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080
}
location ~ /vod/ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8081
}
}4.nginx负责均衡配置
通过http块下的upstream属性进行配置实现
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
upstream backend {
server 127.0.0.1:8081 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=10s;
server 127.0.0.1:8082 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=10s;
# 可选的其他参数
# least_conn; # 使用最少连接的服务器
# ip_hash; # 根据客户端IP进行哈希,确保来自同一IP的请求总是发送到同一台服务器
# keepalive 32; # 每个worker进程保持的最大空闲连接数
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html/dist;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /api/ {
rewrite ^/api/(.*)$ /$1 break;
proxy_pass http://backend;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header REMOTE-HOST $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
}
location /upload/ {
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
}
}
5.nginx 负载均衡分配服务器策略
5.1 轮询(默认)
每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器 down 掉,能自动剔除。
upstream myserver {
server 127.0.0.1:8081;
server 127.0.0.1:8082;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name 127.0.0.1;
location / {
root html;
proxy_pass http://myserver;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}5.2 weight
weight 代表权重, 默认为 1,权重越高被分配的客户端越多
upstream myserver {
server 127.0.0.1:8081 weight=10;
server 127.0.0.1:8082 weight=10;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name 127.0.0.1;
location / {
root html;
proxy_pass http://myserver;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}5.3 ip_hash
ip_hash 每个请求按访问 ip 的 hash 结果分配,这样每个访客固定访问一个后端服务器
upstream myserver {
server 127.0.0.1:8081;
server 127.0.0.1:8082;
ip_hash;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name 127.0.0.1;
location / {
root html;
proxy_pass http://myserver;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}5.4 fair(第三方)
fair(第三方),按后端服务器的响应时间来分配请求,响应时间短的优先分配。
upstream myserver {
server 127.0.0.1:8081;
server 127.0.0.1:8082;
fair;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name 127.0.0.1;
location / {
root html;
proxy_pass http://myserver;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}6.nginx日志分割配置
server {
listen 80;
server_name 127.0.0.1;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
# 请求日志按天/按小时/按分钟/按秒分割
if ($time_iso8601 ~ "^(\d{4})-(\d{2})-(\d{2})T(\d{2}):(\d{2}):(\d{2})")
{
set $year $1;
set $month $2;
set $day $3;
set $hour $4;
set $minutes $5;
set $seconds $6;
}
access_log ./logs/nginx-access_$year-$month-$day.log;
# 错误日志配置
error_log ./logs/nginx-access-error.log;
}参考资料
- Nginx反向代理配置去除前缀-百度开发者中心 (baidu.com)
- Nginx 负载均衡演示之 upstream 参数 & location 参数 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
- Nginx--upstream健康检查 - 心恩惠动 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
- nginx日志切割/分割,按天生成&定期删除日志_nginx 日志按天切割-CSDN博客
- nginx学习,看这一篇就够了:下载、安装。使用:正向代理、反向代理、负载均衡。常用命令和配置文件,很全-CSDN博客
- Nginx——访问日志、错误日志、日志文件切割_nginx错误日志文件太大了怎么办-CSDN博客
- 一文理清nginx中的location配置(系列一) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
- 全网最全最完整Nginx 配置文件nginx.conf中文详解-CSDN博客
- nginx 配置相关详解_nginx 配置详解-CSDN博客
- Nginx配置——反向代理_nginx反向代理-CSDN博客

评论 (0)